
Now let’s test the SNMP configuration try running the following two commands: snmpwalk -v 2c -c idv90we3rnov90wer -O e 127.0.0.1. Configure SNMP to start when the server boots: chkconfig snmpd on. Exit vim, and restart the SNMP service to reload the new configuration file: service snmpd restart.To enable SNMP traps, follow the steps below in the Configuration mode of the Router/Switch: First, set the host to which the traps have to be sent using the folowing command: snmp-server host version where, refers to the IP Address of the device to which the traps have to be sent.CiSCOMDSSW1(config)# snmp-server host 168.50.31.100 traps version 2 I77V5eRAUEAa udp-port 162 CiSCOMDSSW1(config.
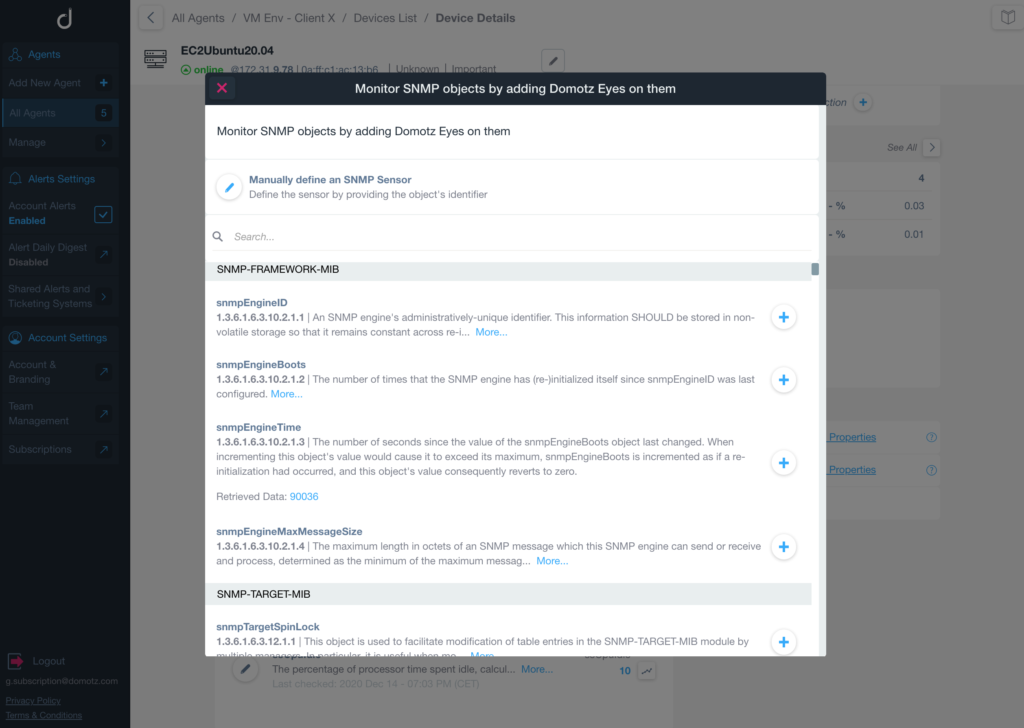
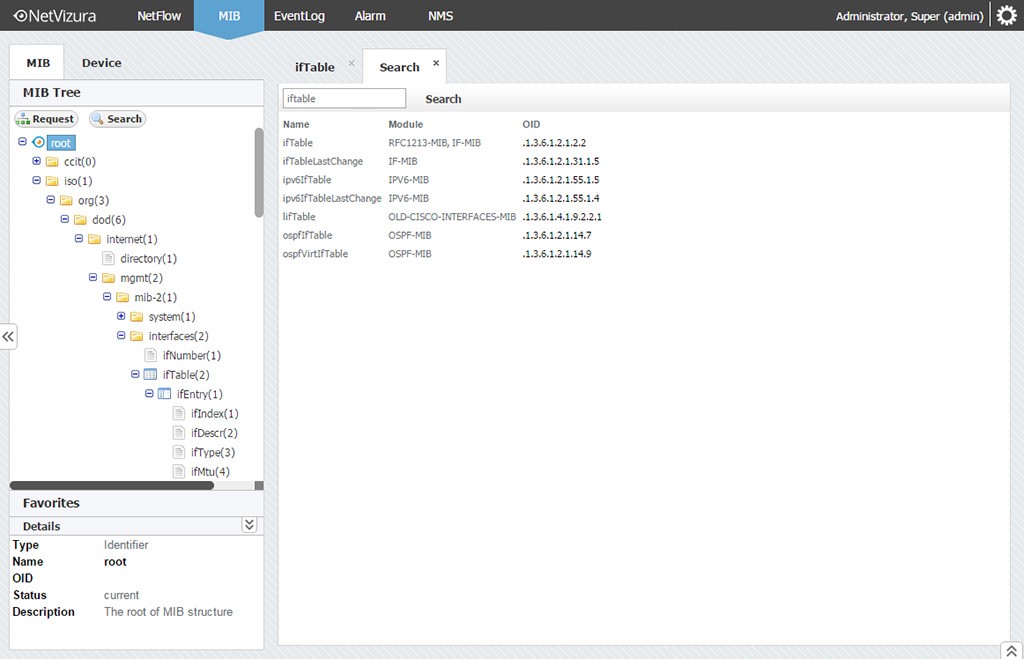
SNMP version 3 (SNMPv3) adds some new commands to the CLI for configuring SNMPv3 functions. (See the Access Security Guide for your switch.) If you want to restrict access to one or more specific nodes, you can use the IP Authorized Manager feature for the switch. In this case, all management stations using the correct User and community name may access the switch with the View and Access levels that have been set for that community. In some networks, authorized IP manager addresses are not used. Enable SNMPv3 for operation on the switch (see Enabling SNMPv3).Ĭonfigure the appropriate SNMP users (see SNMPv3 users).Ĭonfigure the appropriate SNMP communities (see SNMPv3 communities).Ĭonfigure the appropriate trap receivers (see SNMP notifications).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
